Artificial Intelligence
Industry Standards

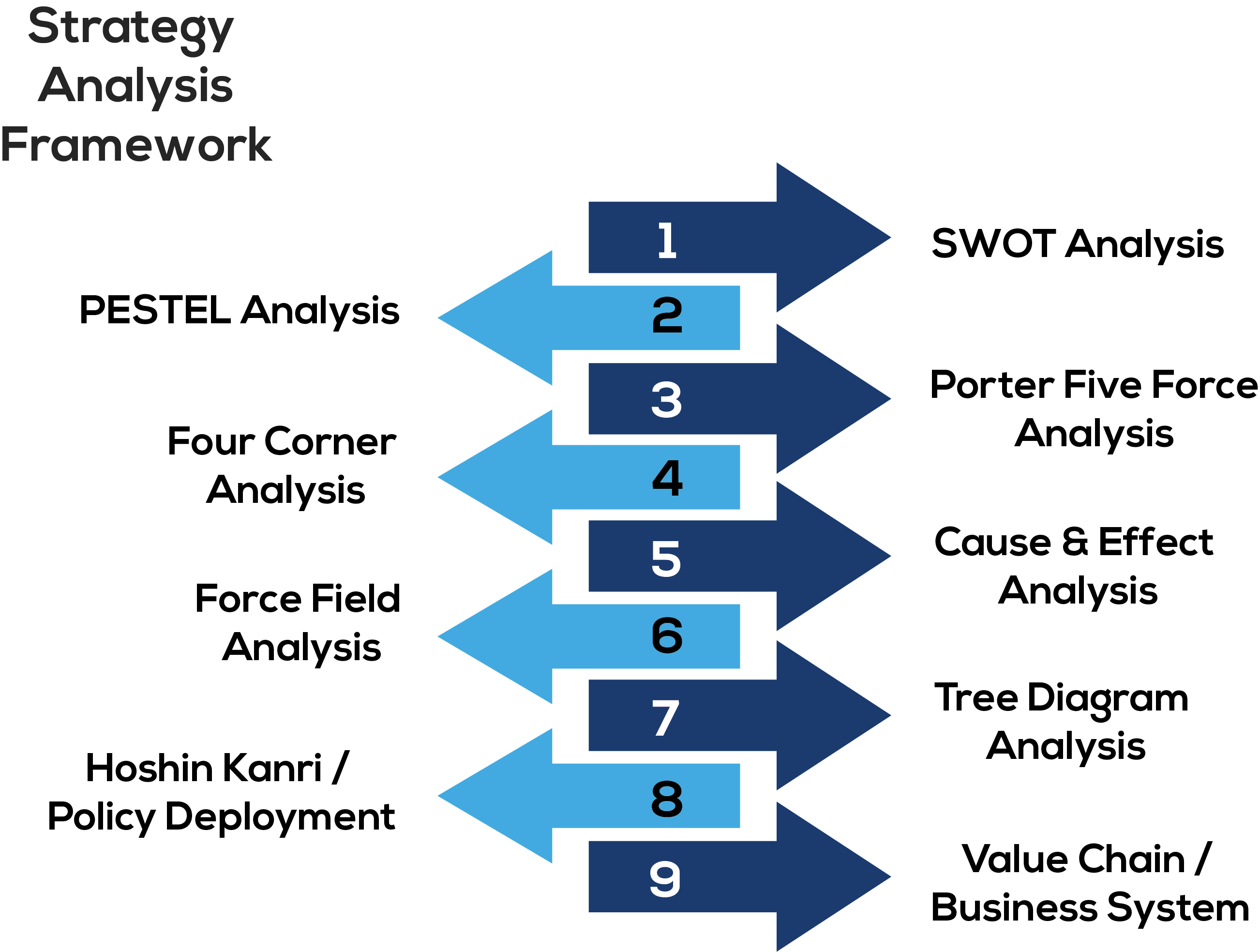
Strategy Analysis is the primary step in strategy planning process. Analysis models are useful tools and techniques that can help you understand your organisational environment and think more strategically about your business. There are many techniques used available, but some are used frequently. The most popular techniques are supported by fruiStrategy.
SWOT Analysis: SWOT analysis (or SWOT matrix) is a strategic planning technique used to help an organization identify Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to business competition, business environment, or project planning. This technique is designed for use in the preliminary stages of decision-making processes and can be used as a tool for evaluation of the strategic position of organizations of all kinds. It is intended to identify the internal and external factors that are favourable and unfavourable to achieving the objectives of the business. Users of a SWOT analysis often ask and answer questions to generate meaningful information for each category to make the tool useful and identify their competitive advantage. fruiStrategy facilitates SWOT analysis exercise and enables to keep track of all historical information to know how the organization strategy planning process is progressing.
PESTEL Analysis: A PESTEL analysis is a strategic framework commonly used to evaluate the business environment in which a firm operates. Traditionally, the framework was referred to as a PEST analysis, which was an acronym for Political, Economic, Social, and Technological; in more recent history, the framework was extended to include Environmental and Legal factors.
The framework is used by management teams and boards in their strategic planning processes and enterprise risk management planning. PESTEL analysis is also a very popular tool among management consultants to help their clients develop innovative product and market initiatives, as well as within the financial analyst community, where factors may influence model assumptions and financing decisions.
Porter Five Force Analysis: Porter's Five Forces Framework is a method of analysing the operating environment of a competition of a business. It draws from organization to derive five forces that determine the competitive intensity and, therefore, the attractiveness of an industry in terms of its profitability. An "unattractive" industry is one in which the effect of these five forces reduces overall profitability. The most unattractive industry would be one approaching "pure competition", in which available profits for all firms are driven to normal profit levels. The five-forces perspective is associated with its originator, Michael E. Porter of Harvard University.
Porter's Five Forces is a model that identifies and analyses five competitive forces and they are; Competition in the industry, Potential of new entrants into the industry, Power of suppliers, Power of customers, Threat of substitute products.
Four Corner Analysis: Porter's four corners model is a predictive tool designed by Michael Porter that helps in determining a competitor's course of action. Unlike other predictive models which predominantly rely on a firm's current strategy and capabilities to determine future strategy, Porter's model additionally calls for an understanding of what motivates the competitor. This added dimension of understanding a competitor's internal culture, value system, mindset, and assumptions helps in determining a much more accurate and realistic reading of a competitor's possible reactions in a given situation.
The four corners of the model are Motivation - Drivers, Motivation – management assumptions, Actions – strategy, Actions – capabilities. fruiStrategy enables the strategy team to maintain four criteria items along with all required information

Cause & Effect Analysis: Cause and effect analysis, also called a “cause and effect diagram,” is an assessment tool that combines brainstorming and mind mapping techniques to explore the possible causes of an issue. It was developed by Kaoru Ishikawa, a quality management pioneer in the 1960s and originally used as a quality control tool.
While cause and effect analysis is not exclusive to any industry, many professionals in management and business use this analysis method. They identify problems in the workplace or a project and investigate possible causes through brainstorming sessions and visual aids.
Force Field Analysis: Force field analysis is a basic tool for root cause analysis that can help you take action once the root cause has been identified. The technique is based on the assumption that any situation is the result of forces for and against the current state being in equilibrium. Countering the opposing forces and/or increasing the favourable forces will help induce a change by reinforcing positives and eliminating or reducing negatives. fruiStrategy helps managers to perform Force Field Analysis.
Tree Diagram Analysis: A tree diagram is a new management planning tool that depicts the hierarchy of tasks and subtasks needed to complete and objective. The tree diagram starts with one item that branches into two or more, each of which branch into two or more, and so on. The finished diagram bears a resemblance to a tree, with a trunk and multiple branches. Tree diagram can be used in following scenarios.
Value Chain/Business System: Value chain analysis is a tool that business owners use to break down each process their business uses. This analysis can be used to improve the business’s individual processes, enhancing the company’s efficiency and establishing a competitive advantage.
Industry Standards
Industry Standards
Industry Standards
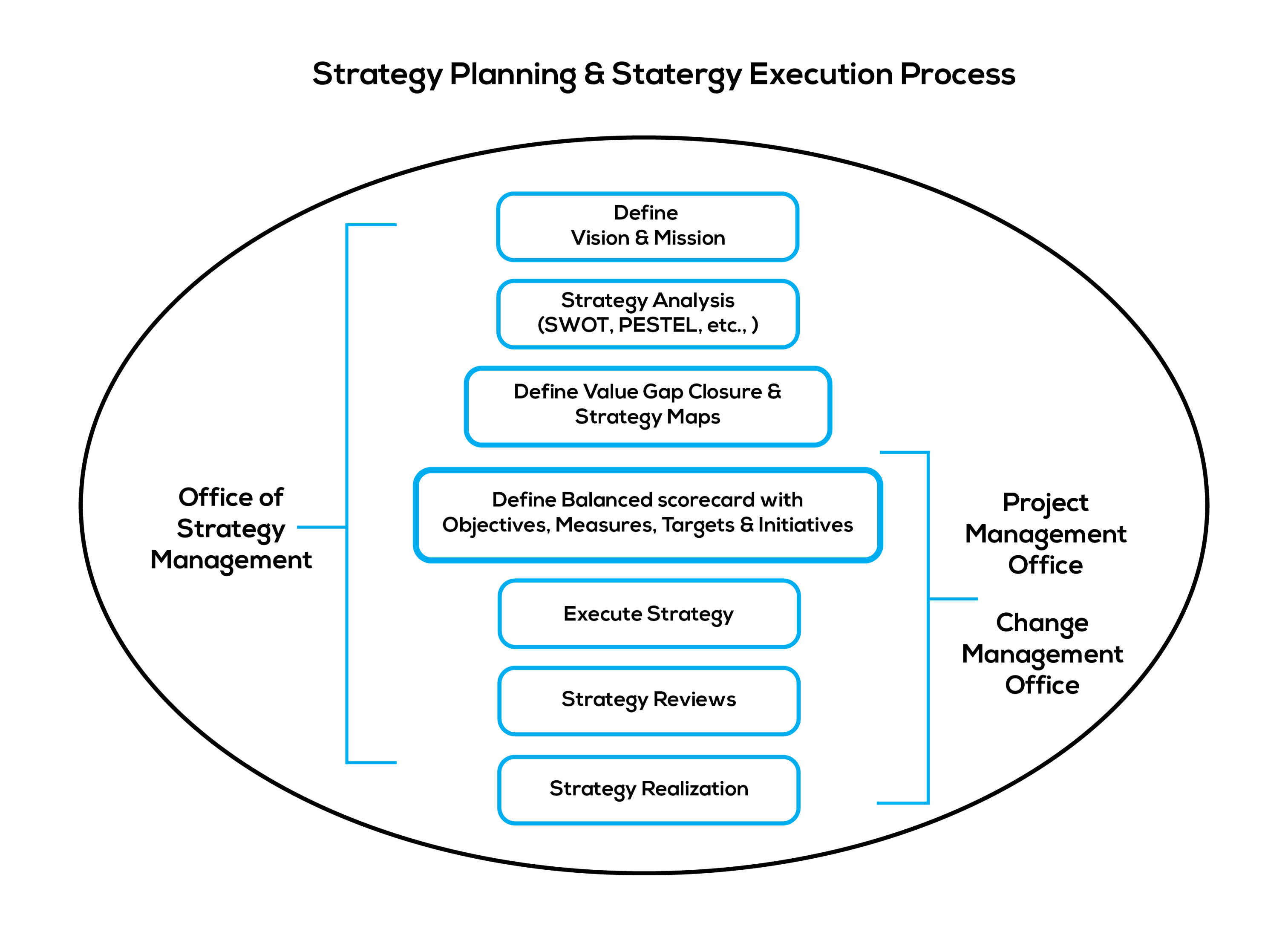
Consulting for all steps in strategy execution which include strategy planning, strategy translation, strategy reviews, PMO processes, risk management, strategy refresh, personal scorecards and others.
Implementation of strategy execution process aligning with all best practices which include Execution Premium, OKR, Enterprise PMO, Enterprise Risk Management, Personal Scorecards, and Strategy Analysis tools.
Integration with all complementing solutions and data sources to have seamless flow of data to make data available on time to enable better decision making.
Software solution which is comprehensive, easy to implement, easy to maintain empowered by latest technologies which include AI/ML, process mining, mobility, API enabled.

© 2023 - Data Labs America all rights reserved.
